Agent Instructions
Overview
VoltAgent supports three approaches for defining agent instructions. Each approach addresses different requirements around flexibility, team collaboration, and deployment workflows.
The Three Approaches
| Approach | Definition | Context Access | Team Workflow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static Instructions | Hardcoded string | No | Code-based |
| Dynamic Instructions | Function with runtime context | Yes | Code-based |
| VoltOps Management | Externally managed prompts | Yes | Platform-managed |
Static Instructions
Static instructions are literal strings assigned to the instructions property.
import { Agent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const agent = new Agent({
name: "SupportAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: "You are a customer support agent. Help users with their questions.",
});
Type signature:
instructions: string;
When to Use
Use static instructions when:
- Agent behavior is consistent across all interactions
- No runtime context is needed
- Instructions rarely change
- Team members edit prompts through code reviews
Avoid when:
- Different users need different behavior
- Instructions depend on runtime data (user tier, time, location)
- Non-technical team members need to edit prompts
- You need prompt versioning outside of code commits
Dynamic Instructions
Dynamic instructions are functions that receive runtime context and return instructions.
Returning Strings
Functions can return a plain string based on context:
const agent = new Agent({
name: "SupportAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: async ({ context }) => {
const userTier = context.get("userTier") || "basic";
if (userTier === "premium") {
return "You are a premium customer support agent. Provide detailed explanations and prioritize this customer's requests.";
}
return "You are a customer support agent. Provide helpful but concise answers.";
},
});
Using with context:
const premiumContext = new Map();
premiumContext.set("userTier", "premium");
const response = await agent.generateText("I need help", {
context: premiumContext,
});
Returning PromptContent Objects
Functions can also return PromptContent objects for text or chat-based instructions.
Text type:
const agent = new Agent({
name: "SupportAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: async ({ context }) => {
return {
type: "text",
text: "You are a customer support agent.",
};
},
});
Chat type with multiple messages:
import { Agent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const agent = new Agent({
name: "ChatAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: async () => {
return {
type: "chat",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{
role: "user",
content: "Hello!",
},
{
role: "assistant",
content: "Hi! How can I help you today?",
},
],
};
},
});
Chat type with provider-specific options:
import { Agent } from "@voltagent/core";
import { anthropic } from "@ai-sdk/anthropic";
const agent = new Agent({
name: "CachedAgent",
model: anthropic("claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219"),
instructions: async () => {
return {
type: "chat",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: "Long system prompt that should be cached...",
providerOptions: {
anthropic: {
cacheControl: { type: "ephemeral", ttl: "5m" },
},
},
},
],
};
},
});
Type signature:
instructions: (options: DynamicValueOptions) => Promise<string | PromptContent>;
interface DynamicValueOptions {
context: Map<string | symbol, unknown>;
prompts: PromptHelper;
}
interface PromptContent {
type: "text" | "chat";
text?: string;
messages?: ChatMessage[];
}
When to Use
Use dynamic instructions when:
- Agent behavior depends on user properties (tier, role, preferences)
- Instructions need runtime data (time, location, session state)
- Different tenants require different behavior
- Conditional logic determines instruction content
Avoid when:
- Multiple non-technical stakeholders need to edit prompts
- You need prompt version history outside of code
- Collaborative prompt editing is required
- Prompts should update without deploying code
VoltOps Prompt Management
VoltOps separates prompt content from application code. Prompts are created and versioned in the VoltOps platform, then fetched at runtime.
Setup
1. Get API keys:
Sign up at console.voltagent.dev and navigate to Settings → Projects.
2. Configure environment:
VOLTAGENT_PUBLIC_KEY=pk_your_public_key_here
VOLTAGENT_SECRET_KEY=sk_your_secret_key_here
Create a Prompt
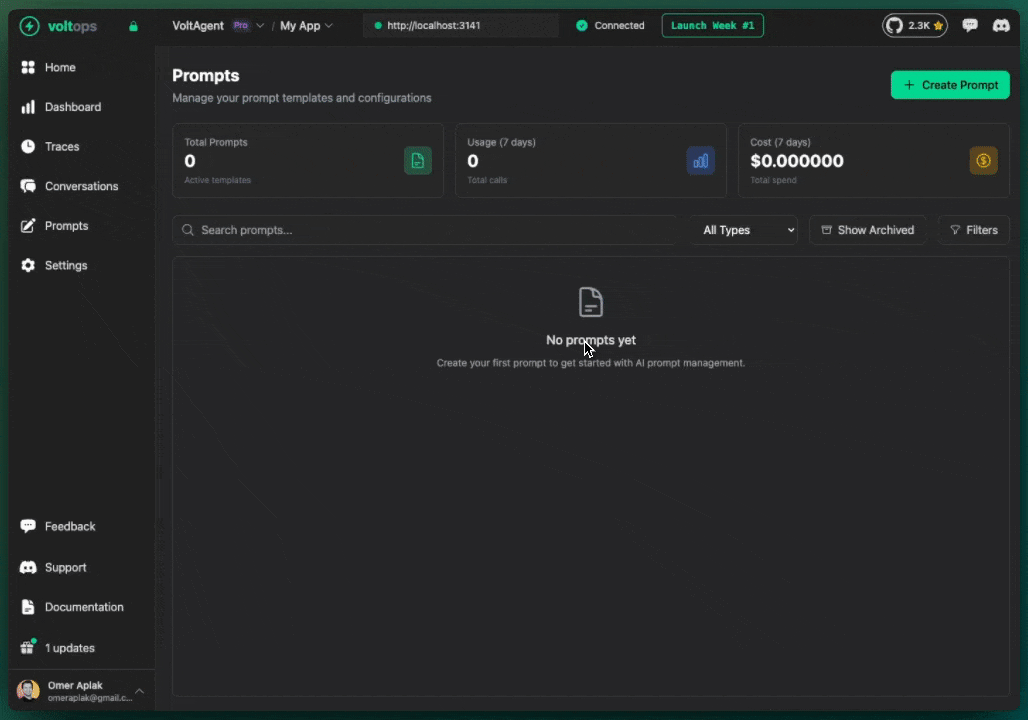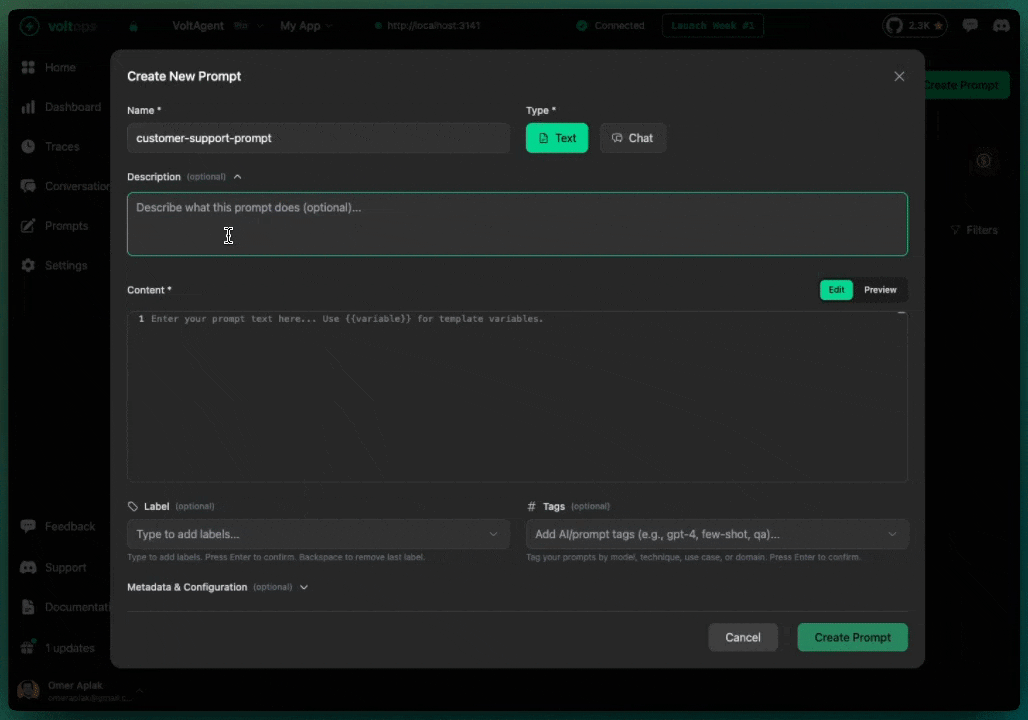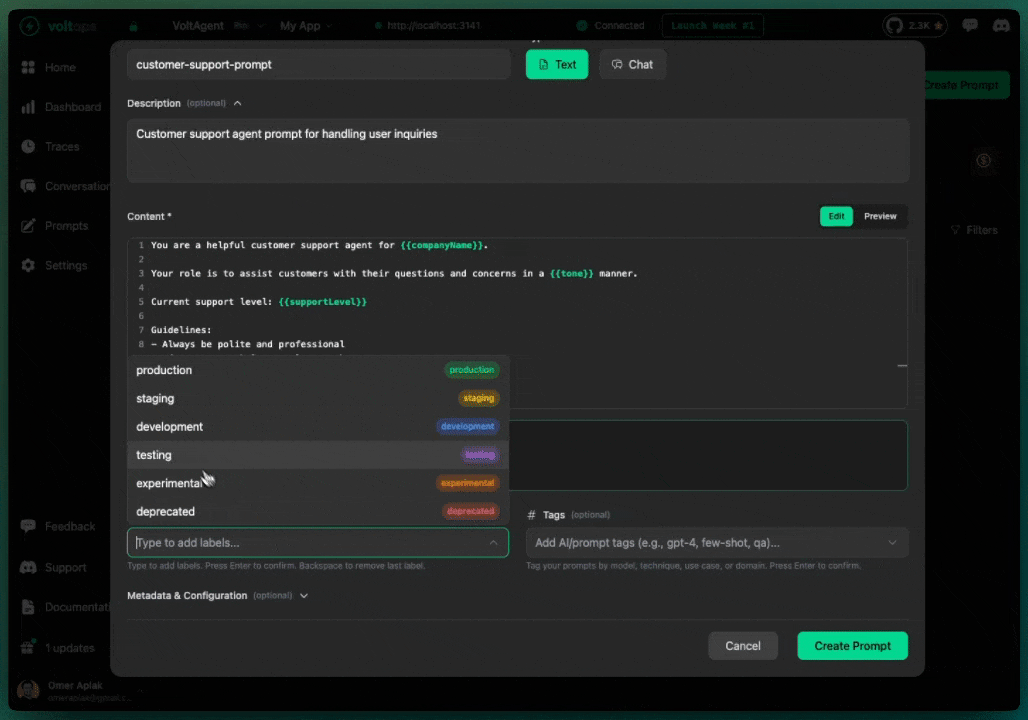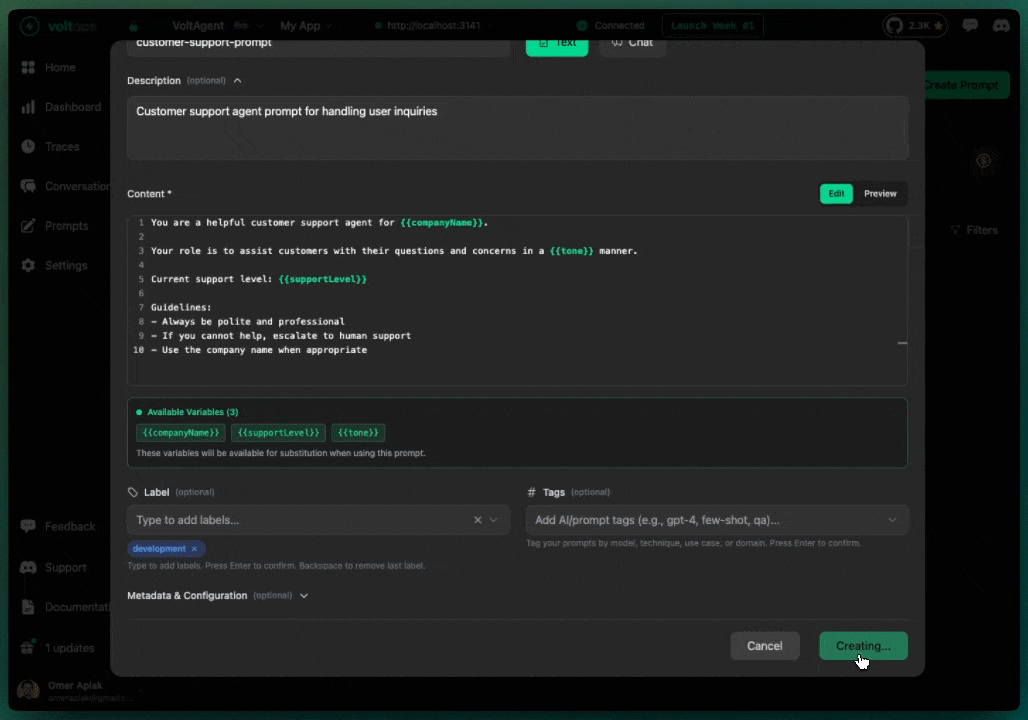
- Navigate to console.voltagent.dev/prompts
- Click "Create Prompt"
- Fill in details:
- Name:
customer-support-prompt - Type:
TextorChat - Content: Your prompt with optional template variables like
{{companyName}}
- Name:
- Set initial label (e.g.,
development) - Click "Create Prompt"
Use in Code
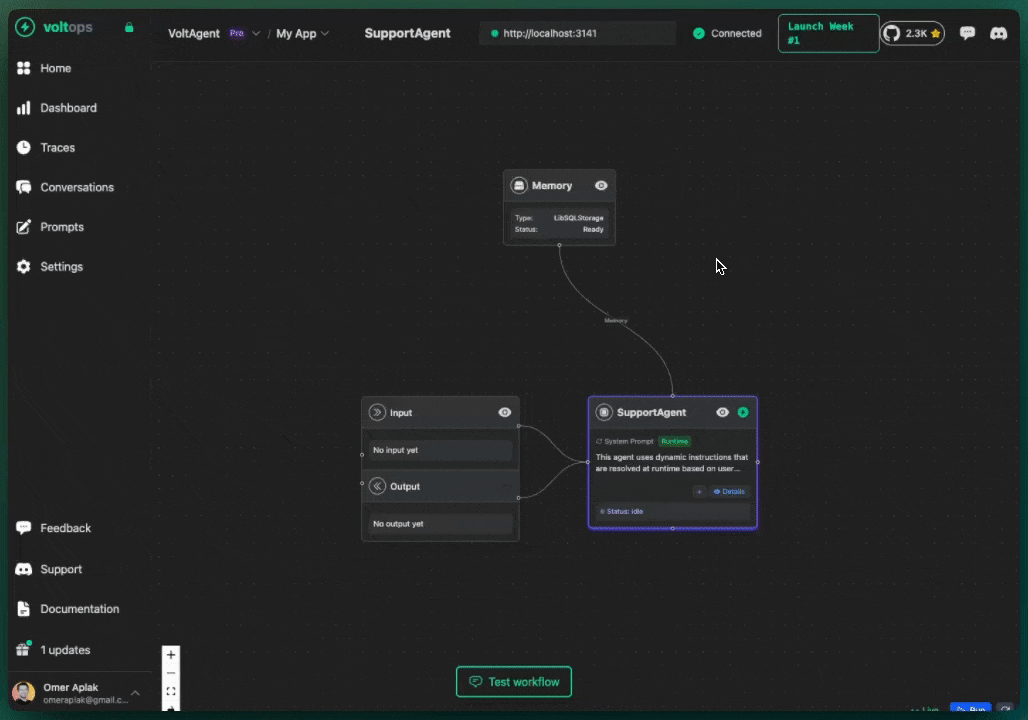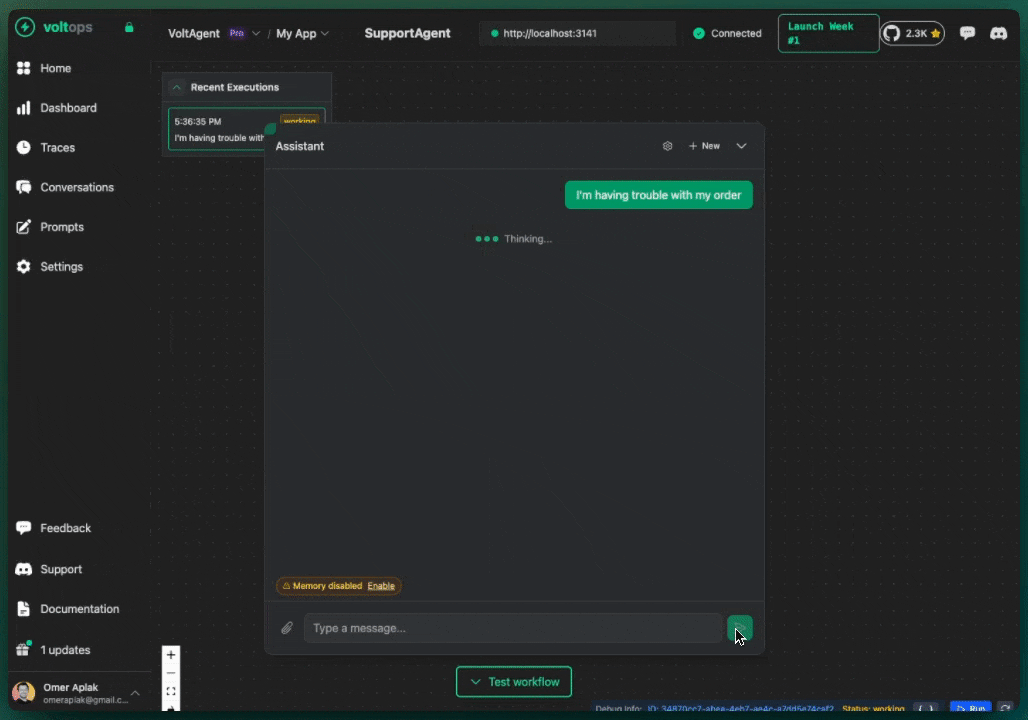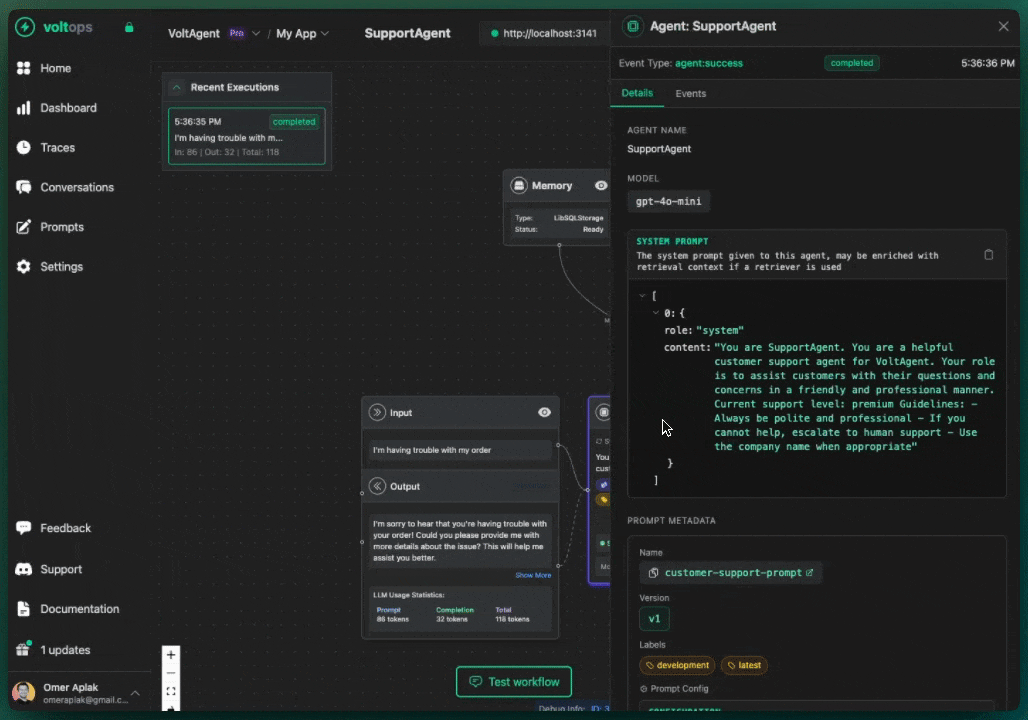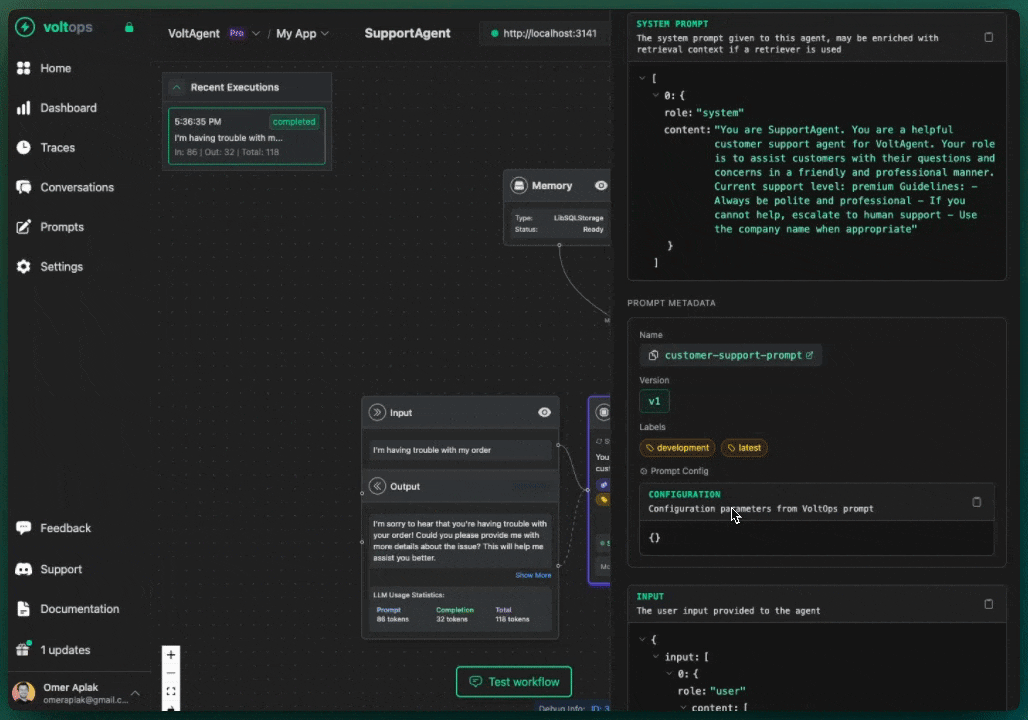
import { Agent, VoltAgent, VoltOpsClient } from "@voltagent/core";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const voltOpsClient = new VoltOpsClient({
publicKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_PUBLIC_KEY,
secretKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_SECRET_KEY,
prompts: true,
promptCache: {
enabled: true,
ttl: 300, // 5 minutes
},
});
const agent = new Agent({
name: "SupportAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "customer-support-prompt",
variables: {
companyName: "VoltAgent Corp",
tone: "professional",
},
});
},
});
const voltAgent = new VoltAgent({
agents: { agent },
voltOpsClient: voltOpsClient,
});
Alternative: Agent-level VoltOpsClient
const agent = new Agent({
name: "SupportAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "customer-support-prompt",
variables: { companyName: "VoltAgent Corp" },
});
},
voltOpsClient: voltOpsClient,
});
Direct VoltOpsClient access:
const voltOpsClient = new VoltOpsClient({
publicKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_PUBLIC_KEY,
secretKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_SECRET_KEY,
});
const content = await voltOpsClient.prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "customer-support-prompt",
variables: { companyName: "VoltAgent Corp" },
});
console.log("Prompt content:", content);
Versioning
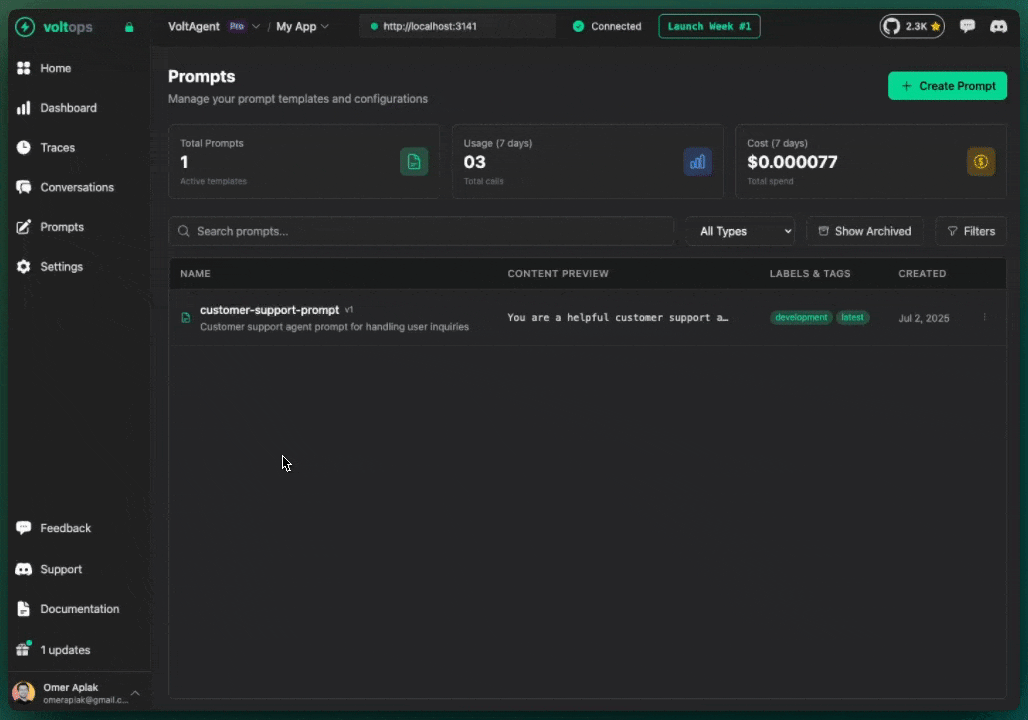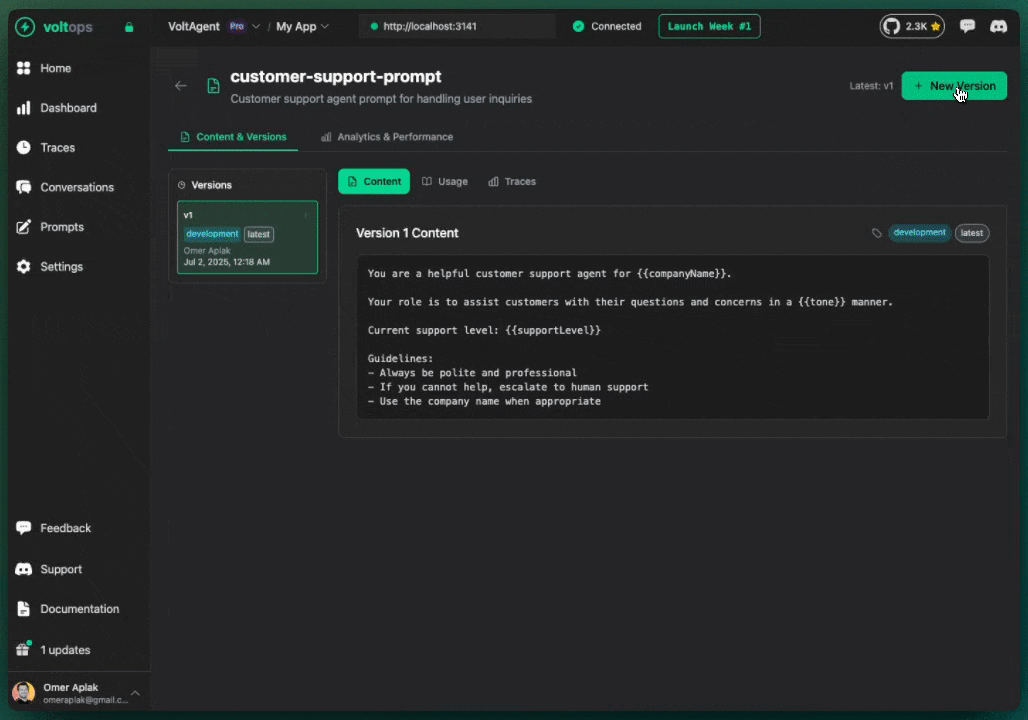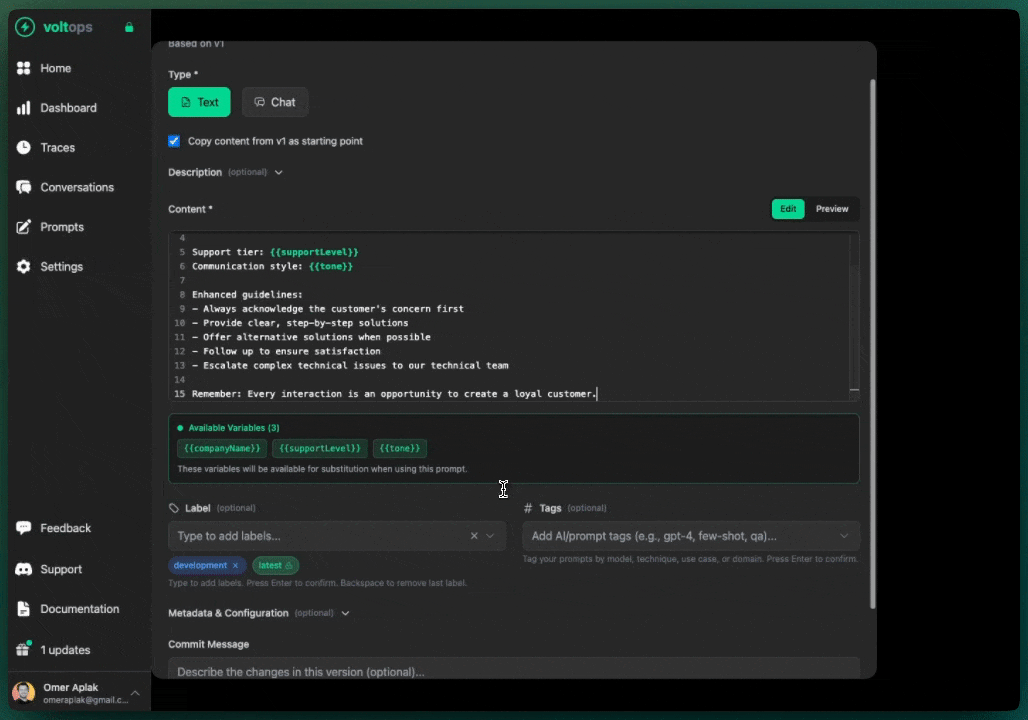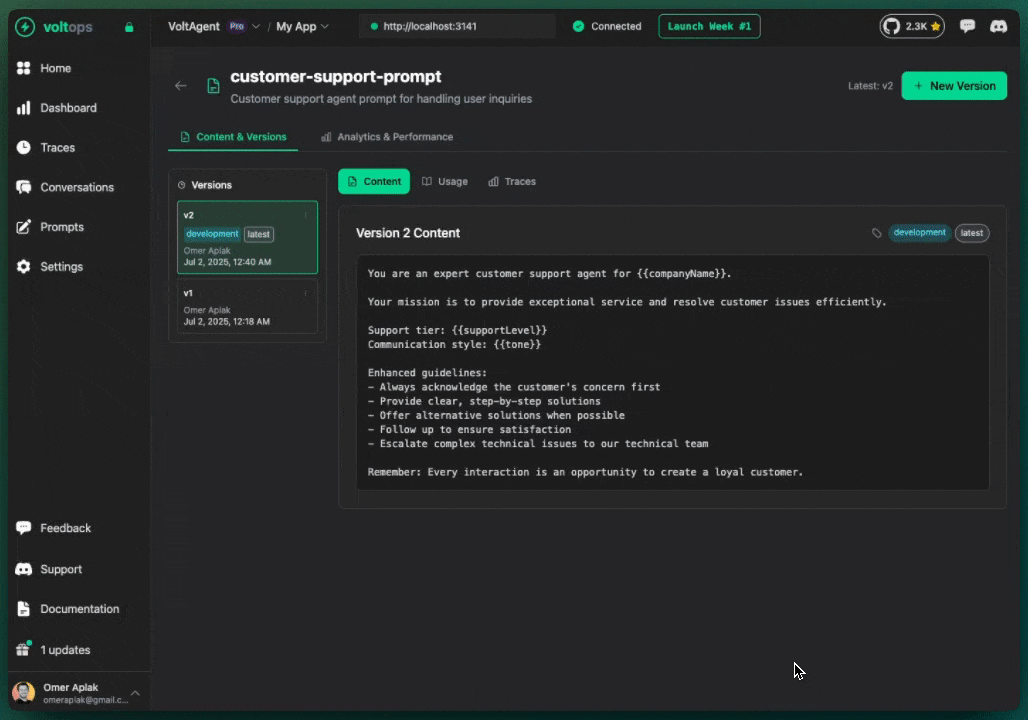
Create new versions through the console:
- Open prompt detail page
- Click "New Version"
- Modify content
- Add commit message
- Click "Create Version"
Caching
VoltOps caches prompts at two levels.
Global cache (VoltOpsClient):
const voltOpsClient = new VoltOpsClient({
promptCache: {
enabled: true,
ttl: 300, // Seconds until expiration
maxSize: 100, // Maximum cached prompts
},
});
Per-prompt cache override:
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "customer-support-prompt",
promptCache: { enabled: false }, // Disable cache for this fetch
variables: { companyName: "VoltAgent Corp" },
});
};
Clear cache:
voltOpsClient.prompts.clearCache();
Labels
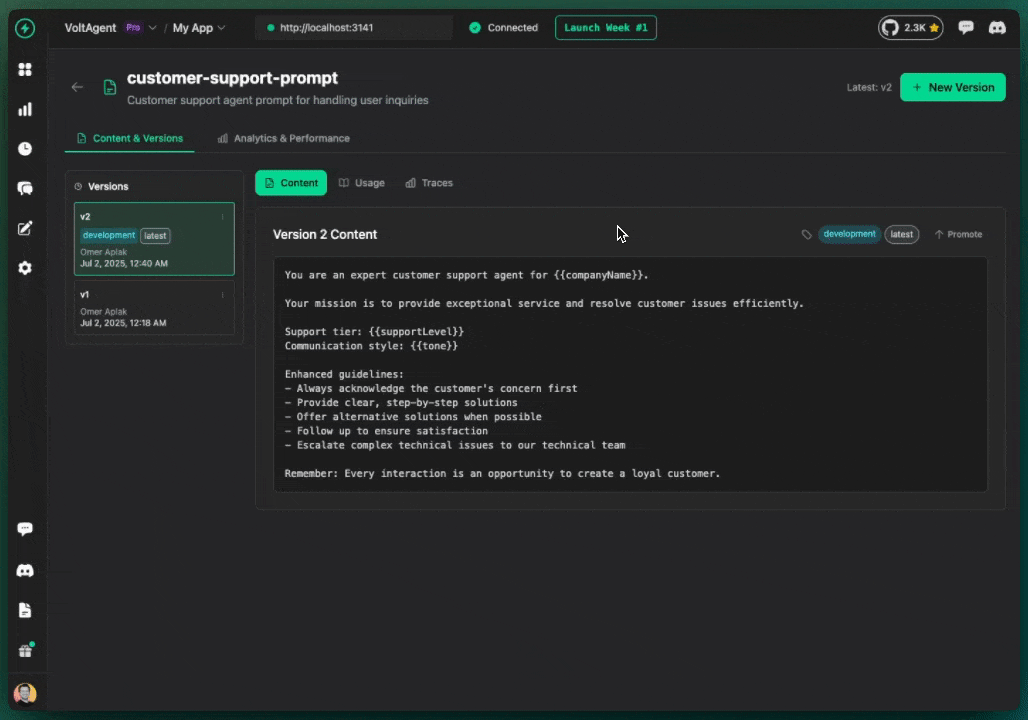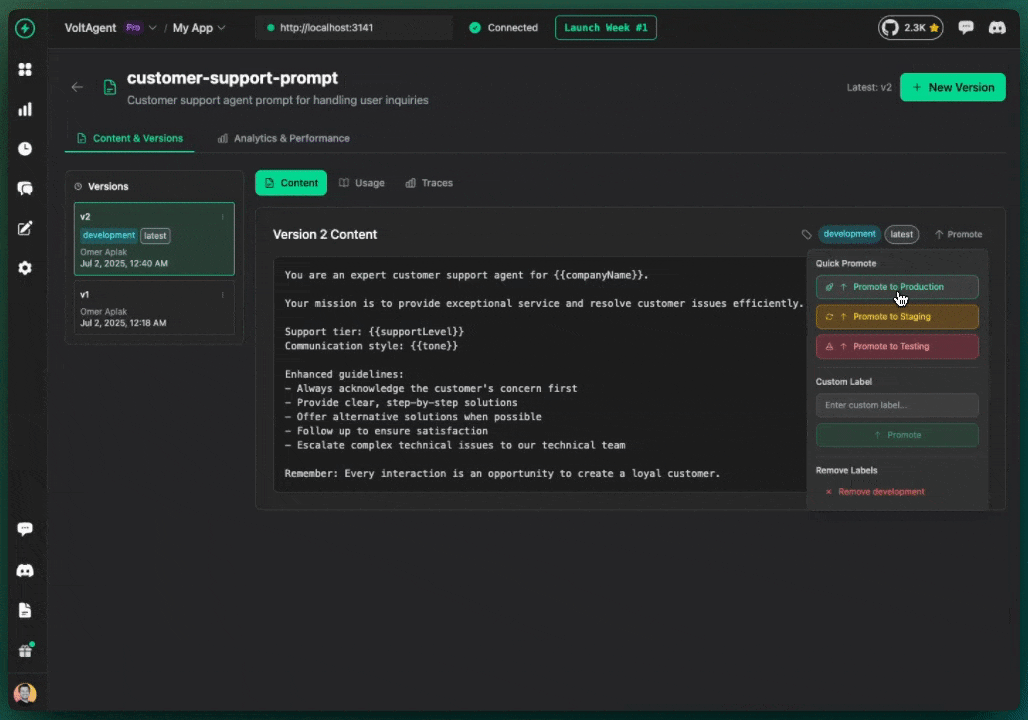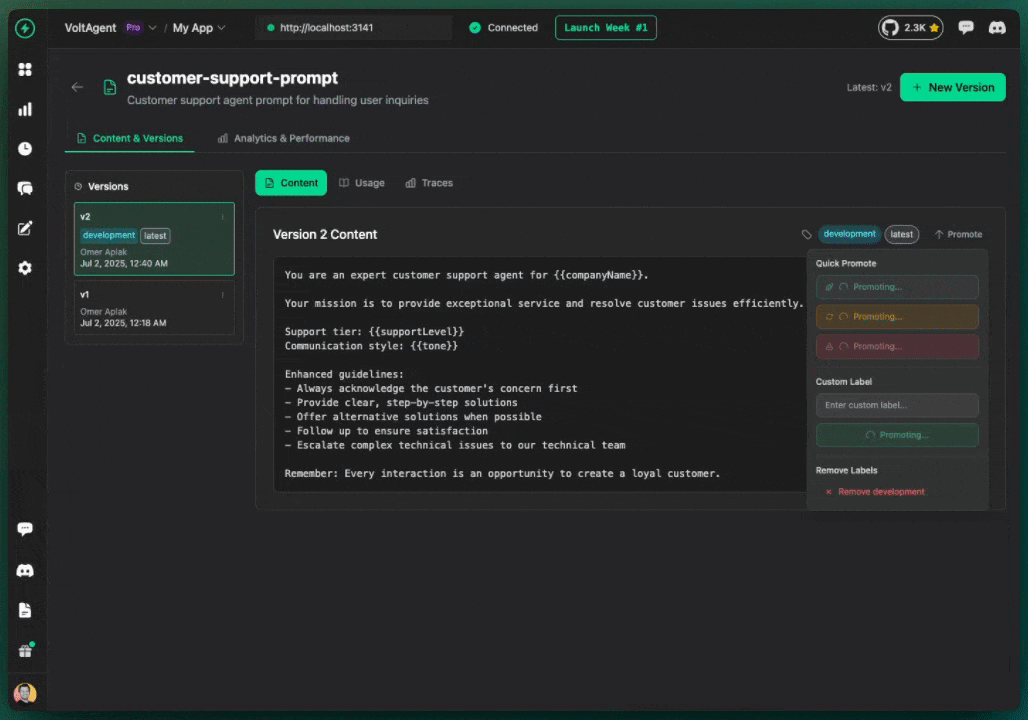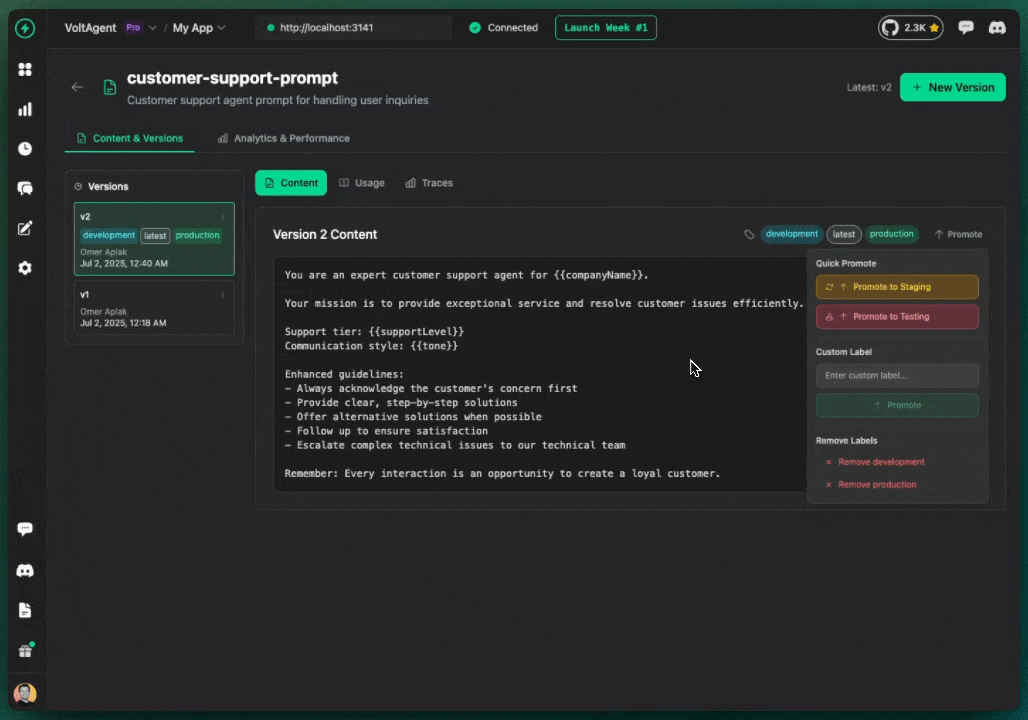
Labels associate versions with environments.
Promote version to label:
- Open prompt detail page
- Find version in history
- Click "⋯" menu
- Select "Promote to Production"
Use labels in code:
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
const label = process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ? "production" : "development";
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "customer-support-prompt",
label: label,
variables: {
/* ... */
},
});
};
Chat Prompts
Chat prompts define multi-message conversations.
Create in console:
- Click "Create Prompt"
- Select type: "Chat"
- Add messages:
[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are {{agentRole}} for {{companyName}}."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Hello, I need help."
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Hello! How can I assist you today?"
}
]
Use in code:
const agent = new Agent({
name: "ChatAgent",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "chat-support-prompt",
variables: {
agentRole: "customer support specialist",
companyName: "VoltAgent Corp",
},
});
},
voltOpsClient: voltOpsClient,
});
When to Use
Use VoltOps when:
- Non-technical team members edit prompts
- Audit trails and approval workflows are required
- Multiple environments need different prompt versions
- Prompt analytics and monitoring are needed
- Managing many prompts across multiple agents
Avoid when:
- External dependencies are not acceptable
- Offline operation is required
- Network latency is a concern (though mitigated by caching)
Best Practices
Versioning
Use descriptive commit messages:
// Avoid
"updated prompt";
"fixed issues";
// Prefer
"Add persona consistency guidelines for customer support";
"Reduce hallucination by adding explicit knowledge boundaries";
Error Handling
Implement fallback strategies:
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
try {
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "primary-prompt",
timeout: 5000,
});
} catch (error) {
console.error("Prompt fetch failed:", error);
return "You are a helpful assistant.";
}
};
Performance
Cache configuration:
// High-frequency prompts: short TTL
await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "chat-greeting",
promptCache: { ttl: 60, enabled: true },
});
// Stable prompts: long TTL
await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "system-instructions",
promptCache: { ttl: 3600, enabled: true },
});
// Dynamic prompts: no cache
await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "personalized-prompt",
promptCache: { enabled: false },
variables: { userId: dynamicUserId },
});
Preload prompts:
const criticalPrompts = ["welcome-message", "error-handler"];
await Promise.all(criticalPrompts.map((name) => prompts.getPrompt({ promptName: name })));
Security
Sanitize template variables:
instructions: async ({ prompts, context }) => {
const sanitizedUserName =
context.get("userName")?.replace(/[<>]/g, "")?.substring(0, 50) || "Guest";
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "personalized-greeting",
variables: { userName: sanitizedUserName },
});
};
Troubleshooting
Prompt not found
// Error: Prompt 'weather-prompt' not found
// Solution: Verify name and existence
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
try {
return await prompts.getPrompt({ promptName: "weather-prompt" });
} catch (error) {
console.error("Prompt fetch failed:", error);
return "Fallback instructions";
}
};
Missing variables
// Error: Variable 'userName' not found
// Solution: Provide all required variables
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "greeting-prompt",
variables: {
userName: context.get("userName") || "Guest",
currentTime: new Date().toISOString(),
},
});
Stale cache
// Problem: Old prompt version still in use
// Solution 1: Clear cache
voltOpsClient.prompts.clearCache();
// Solution 2: Disable cache temporarily
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "urgent-prompt",
promptCache: { enabled: false },
});
// Solution 3: Wait for TTL expiration
Authentication
// Error: Authentication failed
// Solution: Verify environment variables
console.log("Public Key:", process.env.VOLTAGENT_PUBLIC_KEY?.substring(0, 8) + "...");
console.log("Secret Key:", process.env.VOLTAGENT_SECRET_KEY ? "Set" : "Missing");
Debug prompts independently
const voltOpsClient = new VoltOpsClient({
publicKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_PUBLIC_KEY,
secretKey: process.env.VOLTAGENT_SECRET_KEY,
});
try {
const prompt = await voltOpsClient.prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "test-prompt",
});
console.log("Success:", prompt);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Failed:", error);
}
Comparison
| Feature | Static | Dynamic | VoltOps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | String | Function | External platform |
| Context Access | No | Yes | Yes (via function) |
| Runtime Flexibility | None | Full | Full |
| Team Collaboration | Code review | Code review | Platform UI |
| Version Control | Git | Git | VoltOps + Git |
| Non-technical Editing | No | No | Yes |
| Analytics | No | No | Yes |
| Offline Support | Yes | Yes | No |
| External Dependency | No | No | Yes |
Examples
Static (solo developer, consistent behavior):
const agent = new Agent({
instructions: "You are a code reviewer. Focus on security and performance.",
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
});
Dynamic (user-specific behavior):
const agent = new Agent({
instructions: async ({ context }) => {
const tier = context.get("tier");
return tier === "premium"
? "You are a premium support agent with deep technical expertise."
: "You are a support agent providing efficient solutions.";
},
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
});
VoltOps (team collaboration, versioning):
const agent = new Agent({
instructions: async ({ prompts }) => {
return await prompts.getPrompt({
promptName: "customer-support-agent",
label: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ? "production" : "development",
});
},
model: openai("gpt-4o-mini"),
voltOpsClient: voltOpsClient,
});